In today’s digital environment, understanding IP addresses and specific port configurations is crucial for network administrators, developers, and cybersecurity professionals. One such address often seen in local or private environments is 172.16.252.214:4300. This combination of an IP and port number represents a localized communication endpoint used for internal applications, testing, or restricted network access. Knowing how it functions can help prevent misconfigurations, ensure security, and optimize network performance.
What Is 172.16.252.214:4300?
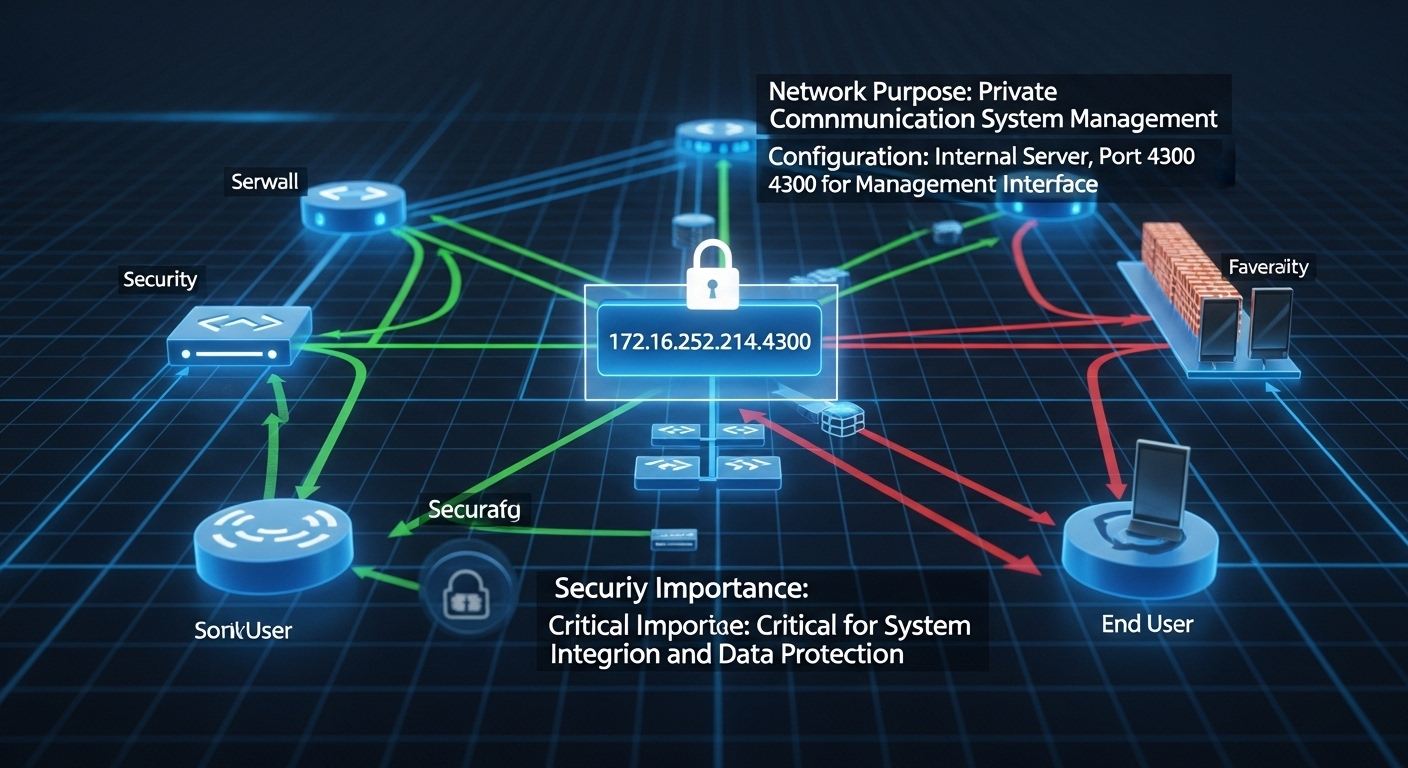
The IP 172.16.252.214:4300 consists of two important elements — the IP address (172.16.252.214) and the port number (4300). The IP part belongs to the private Class B range (172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255), which means it’s not accessible from the public internet. Instead, it’s designed for use within internal networks like organizations, labs, or cloud-based virtual networks. The port number 4300 defines a specific communication channel on that IP, allowing applications to send or receive data in a structured way.
In practice, 172.16.252.214:4300 may be used to host internal tools, run development servers, or manage networked applications. For instance, a database interface, monitoring dashboard, or web testing server could be configured to operate on this port within a secured environment.
Why Is 172.16.252.214:4300 Common in Internal Networks?
Private IPs such as 172.16.252.214:4300 are essential for organizations that need isolated environments. They prevent internal systems from being exposed to the internet, thus reducing the risk of cyberattacks. Many companies use these IPs for backend communication between devices, databases, and servers.
The port number 4300 is not assigned to any default protocol, meaning it’s often chosen for custom applications. This flexibility makes 172.16.252.214:4300 a popular setup among developers who require secure internal testing environments. It ensures that experimental services or in-development tools remain contained within a private framework.
How 172.16.252.214:4300 Works in a Network
When a device within a private network sends a request to 172.16.252.214:4300, the system routes the connection to the machine associated with that address. The port number tells the operating system which service should handle the communication. For example, if a web service is listening on port 4300, it receives all incoming requests directed to 172.16.252.214:4300.
This setup is especially useful in LAN or VPN environments, where developers want to isolate different services. For example, one port might handle an API, another might manage a database, while 172.16.252.214:4300 could serve as an internal monitoring or authentication endpoint.
Security Considerations for 172.16.252.214:4300
Even though 172.16.252.214:4300 is a private IP, it still requires strict security protocols. If improperly configured, such addresses can become vulnerable to insider threats or accidental exposure. Best practices include:
- Firewall configuration: Always restrict access to 172.16.252.214:4300 to authorized users only.
- Encryption: Use SSL/TLS to secure communication over the port.
- Regular monitoring: Keep an eye on unusual traffic patterns targeting 172.16.252.214:4300.
- Access control: Assign roles and permissions to users who can interact with the service.
Securing 172.16.252.214:4300 ensures that sensitive internal operations remain protected and isolated from external risks.
Use Cases of 172.16.252.214:4300
- Internal Testing: Developers use 172.16.252.214:4300 to test new web applications before deploying them publicly.
- Database Access: The address might be assigned to an internal database port, providing controlled access.
- System Monitoring: IT teams can use 172.16.252.214:4300 to host dashboards that track resource usage or network performance.
- API Development: Custom APIs within corporate networks often run on private IPs like 172.16.252.214:4300 for secure internal communication.
Each scenario highlights the versatility and importance of maintaining private IPs within organizational infrastructures.
Troubleshooting 172.16.252.214:4300 Connectivity Issues
If devices cannot connect to 172.16.252.214:4300, several potential causes should be checked. First, ensure that the server hosting the address is active and the service bound to port 4300 is running. Next, verify that the local network firewall allows traffic to that port. Finally, confirm that IP configurations across devices are aligned with the same subnet range as 172.16.252.214:4300.
Addressing these factors quickly restores connectivity and prevents downtime for internal systems relying on this endpoint.
Conclusion
In summary, 172.16.252.214:4300 represents a crucial example of how private IPs and port numbers function within secure networks. It enables safe, efficient communication between internal systems, fosters development without public exposure, and enhances control over organizational resources. Whether used for testing, monitoring, or application hosting, understanding and managing 172.16.252.214:4300 is key to maintaining network integrity and performance.